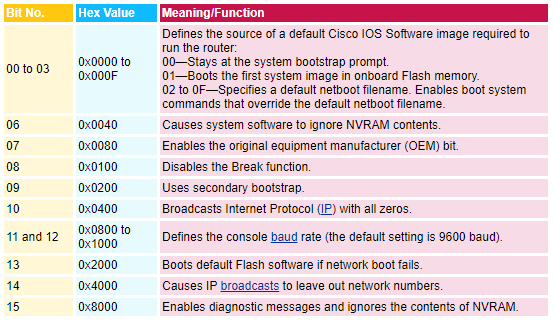
The lowest four bits of the 16-bit configuration register (bits 3, 2, 1, and 0) form the boot field. The following boot field values determine if the router loads an operating system and where it obtains the system image:
- When the entire boot field equals 0-0-0-0 (0x0), the router does not load a system image. Instead, it enters ROM monitor or "maintenance" mode, from which you can enter ROM monitor commands to manually load a system image.
- When the entire boot field equals 0-0-0-1 (0x1), the router loads the boot helper or rxboot image.
- When the entire boot field equals a value between 0-0-1-0 (0x2) and 1-1-1-1 (0xF), the router loads the system image specified by boot system commands in the startup configuration file.
- When the startup configuration file does not contain boot system commands, the router first tries to load a valid image from the default Flash device, and then if one does not exist it tries to load a default system image stored on a network server.
- When loading a default system image from a network server, the router uses the configuration register settings to determine the default system image filename for booting from a network server. The router forms the default boot filename by starting with the word cisco and then appending the octal equivalent of the boot field number in the configuration register, followed by a hyphen (-) and the processor type name (cisconn-cpu). See the appropriate hardware installation guide for details on the configuration register and the default filename.

No comments:
Post a Comment